Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
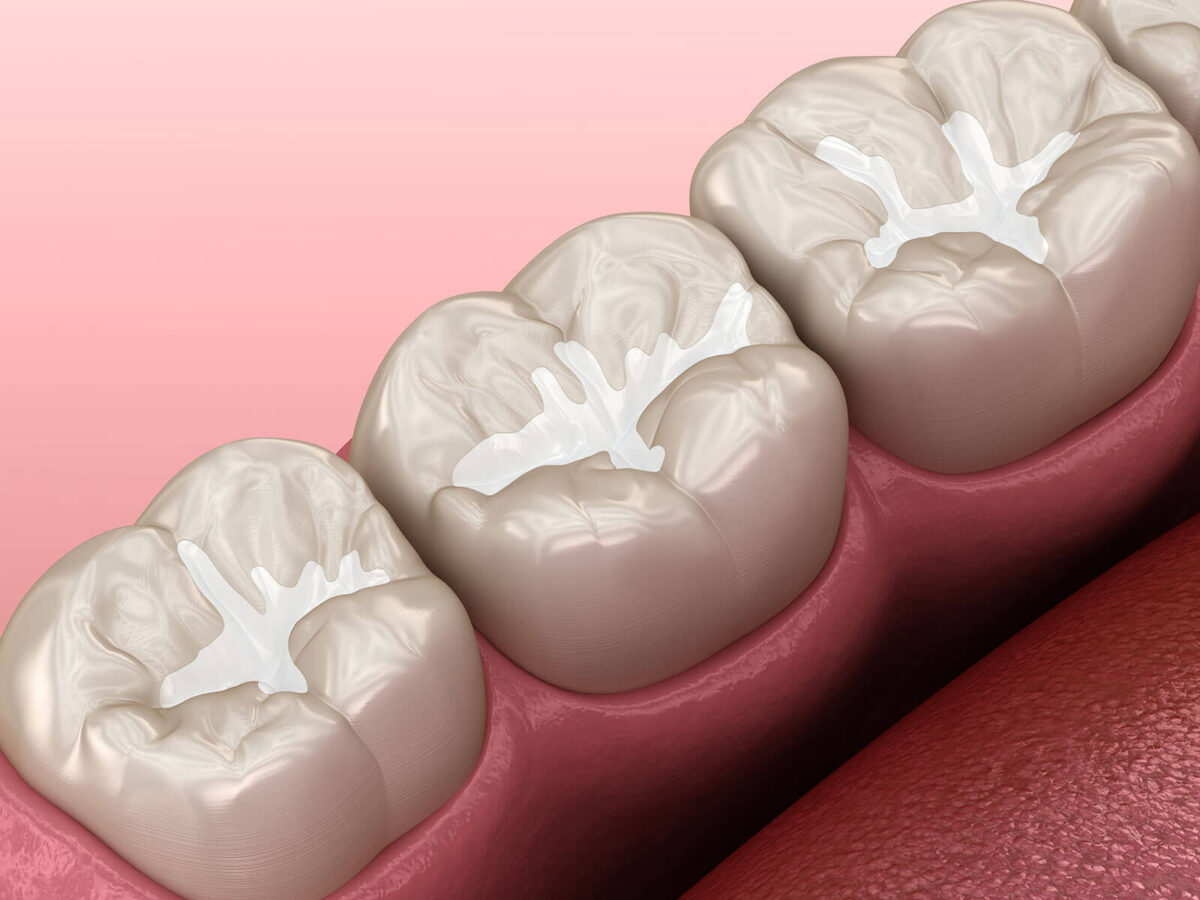
The Role of Sealants In Preventing Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is still a significant concern, particularly among children and adolescents. Dental sealants have emerged as an effective preventive tool in the fight against cavities. In this detailed blog, we’ll look at the relevance of dental sealants, how they’re applied, and their significant influence in protecting teeth from decay.
Dental Hygiene and Preventative Dentistry
Dental hygiene and preventative dentistry are critical to achieving and maintaining oral health. This emphasizes regular treatment and maintenance rather than only addressing dental disorders. Dental sealants are one excellent preventive measure that has gained favor in recent years.
These areas are difficult to properly clean with regular brushing and flossing, putting them vulnerable to decay. Sealants work as a barrier, sealing off these sensitive locations and preventing cavities from forming.
Dental sealants can be applied rapidly and painlessly. First, the dentist cleans and dries the tooth’s surface thoroughly. Then, a specific gel is put into the tooth to aid in the sealant’s bonding. Finally, a curing light is used to cure the sealant material painted onto the tooth. The procedure is usually completed in one visit and is tolerated well by patients of all ages.
How to Understand Tooth Decay:
Cavitation Formation:
- Bacterial Action: In the mouth, harmful bacteria produce acids that erode tooth enamel.
- Cavity Formation: Cavities arise as a result of enamel deterioration over time.
- Pits and fissures: Deep grooves on chewing surfaces are vulnerable to bacterial buildup. Back teeth, particularly molars and premolars, frequently have complicated architecture that raises the risk of decay.
The Function of Dental Sealants:
- Bacterial Barriers: They form a barrier by sealing pits and cracks, preventing germs and food particles from settling in these sensitive locations.
- Resin Coating Sealant Substance: Sealants are often made of a tooth-colored resin.
- Durable and long-lasting: Once placed, they form a strong shield that can withstand chewing pressures for a long time.
Procedure for Applying:
- Cleaning and etching: To prepare the tooth surface for the sealant, the surface is cleansed, and a mildly acidic solution is applied.
- Application of Sealant: The liquid sealant is applied to the prepared tooth surface.
- Curing: A special light may cure or harden it to ensure the sealant clings securely to the tooth.
Benefits of Dental Sealants:
Decay Prevention:
Sealants provide an efficient barrier against germs and acids, dramatically reducing the chance of cavity formation. When applied early, sealants can stop deterioration before it causes irreversible damage.
Ideal for Adolescents and Children:
Sealants are an important preventive measure, especially for children and adolescents struggling to maintain good oral hygiene. Sealants protect during the cavity-prone years by being applied when molars and premolars erupt.
Conservative Strategy:
Sealants are a conservative method that preserves natural tooth structure. Sealant administration is non-invasive and painless, unlike restorative therapies for cavities.
Cost-Effective:
Sealants are a low-cost preventive strategy that can help you avoid more comprehensive and costly dental treatments in the future. Some dental insurance plans may cover the cost of sealants for children.
Upkeep and longevity:
During routine check-ups, dentists evaluate the condition of sealants. Sealants may need to be redone, and dentists can evaluate when this is essential.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices at Home:
Encourage good dental hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing, and supplement sealants’ preventive impact. In addition, maintaining a balanced diet and limiting sugary snacks benefits oral health even more.
Conclusion:
Dental sealants are an excellent tool for preventing tooth decay, particularly on the susceptible chewing surfaces of molars and premolars. Their use is simple yet effective for protecting teeth, especially for children during their formative years. Sealants help to maintain excellent dental health and reduce the incidence of cavities by forming a solid barrier against bacterial incursion. Regular dental check-ups and proactive oral care practices improve the effectiveness of sealants, ensuring that smiles remain healthy and radiant for many years.
